Colytex, Colistimethate Sodium 2MIU
Lyophilized Powder for solution for Injection, Infusion or Inhalation
DESCRIPTION
Colistimethate Sodium is a sterile parenteral polypeptide antibiotic product which, when reconstituted is suitable for intramuscular, intravenous and inhalation administration.
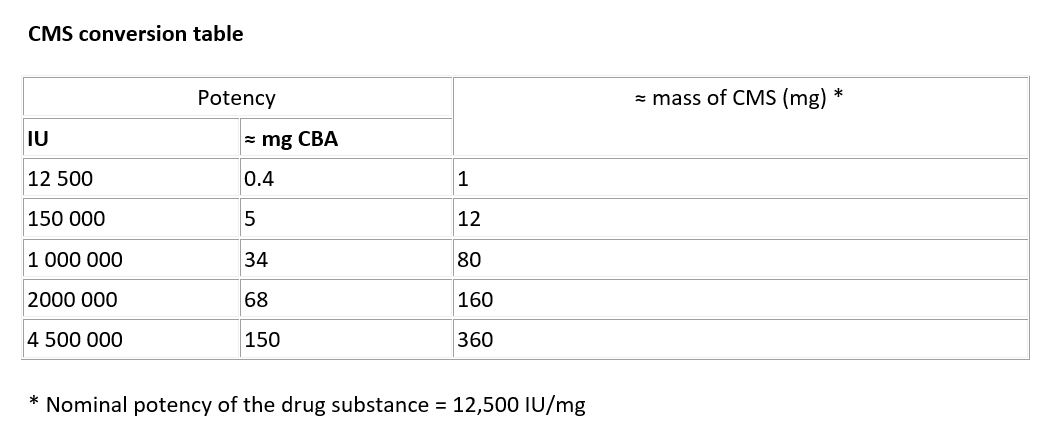
Each vial of 2,000,000 IU Colistimethate sodium, contains approximately 68 mg colistin base activity.
Colistimethate sodium is given by injection to treat some type of serious infections caused by certain bacteria. Colistimethate sodium is given as inhalation to treat chronic chest infection in patients with Colistimethate sodium should use when other antibiotics are not suitable.
MODE OF ACTION
Colistimethate sodium is a cyclic polypeptide antibiotic derived from Bacilus polymyxa var. colistinus and belongs to the polymyxin group. The polymyxin antibiotics are cationic surface-active agents that work by damaging the cell membrane. The resulting physiological effects are lethal to the bacterium.
MICROBIOLOGY
Colistimethate sodium is a surface active agent which penetrates into and disrupts the bacterial cell membrane. It has been shown to have bactericidal activity against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infection as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section:
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms: Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginasa.
SUSCEPTIBILITY TEST
Colistimethate sodium is no longer listed as an antimicrobial for routine testing and reporting by clinical microbiology laboratories.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Colistimethate is indicated for the treatment of acute or chronic infections due to sensitive strains of certain gram-negative bacilli. It is particularly indicated when the infection is caused by sensitive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The antibiotic is not indicated for infections due to Proteus or Neisseria. Colistimethate has proven clinically effective in treatment of infections due to the following gram-negative organisms: Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Colistimethate may be used to initiate therapy in serious infections that are suspected to be due to gram-negative organisms and in the treatment of infections due to susceptible gram-negative pathogenic bacilli.
- Treatment by inhalation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in patients with Cystic fibrosis
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Colistimethate and other antibacterial drugs, Colistimethate should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, localepidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of Colistimethate is contraindicated for patients whit a history of sensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
WARNINGS
Maximum daily dose should not exceed 5 mg/kg/day with normal renal function.
Transient neurological disturbances may occur. These include circumoral paresthesia or numbness, tingling or formication of the extremities, generalized pruritus, vertigo, dizziness, and slurring of speech. For these reasons, patients should be warned not to drive vehicles or use hazardous machinery while on therapy. Reduction of dosage may alleviate symptoms. Therapy need not be discontinued, but such patients should be observed with particular care.
Nephrotoxicity can occur and is probably a dose-dependent effect of Colistimethate sodium. These manifestations of nephrotoxicity are reversible following discontinuation of the antibiotic.
Overdosage can result in renal insufficiency, muscle weakness, and apnea (see OVERDOSAGE section). See PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions subsection for use concomitantly with other antibiotics and curariform drugs.
Respiratory arrest has been reported following intramuscular administration of Colistimethate sodium. Impaired renal function increases the possibility of apnea and neuromuscular blockade following administration of Colistimethate sodium. Therefore, it is important to follow recommended dosing guidelines. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section for use in impairment.
Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Colistimethate, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
Clostridium difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of Clostridium difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against. C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
PRECAUTIONS
-General
Since Colistimethate is eliminated mainly by renal excretion, it should be used with caution when the possibility of impaired renal function exists. The decline in renal function with advanced age should be considered.
When actual renal impairments are present, Colistimethate may be used, but the greatest caution should be exercised and the dosage should be reduced in proportion to the extent of the impairment. Administration of amounts of Colistimethate in excess of renal excretory capacity will lead to high serum levels and can result in further impairment of renal function, initiating a cycle which, if not recognized, can lead to acute renal insufficiency, renal shutdown, and further concentration of the antibiotic to toxic levels in the body. At this point, interference of never transmission at neuromuscular junction may occur and result in muscle weakness and apnea (see OVERDOSAGE section).
- Signs indicating the development of impaired renal function include: diminishing urine output, rising BUN and serum creatinine and decreased creatinine clearance. Therapy with Colistimethate should be discontinued immediately if signs of impaired renal function occur. However, if It is necessary to reinstate the drug, dosing should be adjusted accordingly after drug plasma levels have fallen (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section).
Prescribing Colistimethate in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Caution is advised to administer other nephrotoxic and/or neurotoxic medicine with Colistimethate sodium.
- Drug Interactions
Certain other antibiotics (aminoglycosides and polymyxin) have also been reported to interfere with the nerve transmission at the neuromuscular junction. Based on this reported activity, they should not be given concomitantly with Colistimethate except with the greatest caution.
Curariform muscle relaxants (e.g. tubocurarine) and other drugs, including ether, succinylcholine, gallamine, decamethonium and sodium citrate, potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effect and should be used with extreme caution in patients being treated with Colistimethate.
Sodium cephalothin may enhance the nephrotoxicity of Colistimethate. The concomitant use of sodium cephalothin and Colistimethate should be avoided.
- Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category: C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Since Colistimethate sodium is transferred across the placental barrier in humans, it should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether Colistimethate sodium is excreted in human breast milk. However, Colistin sulphate is excreted in human breast milk. Therefore, caution should be exercise when Colistimethate sodium is administered to nursing woman.
- Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Colistimethate sodium did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautions, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
- Pediatric Use
In clinical studies Colistimethate sodium was administered to the pediatric population (neonates, infants, children and adolescents). Although adverse reaction appears to be similar in the adult and pediatric population, subjective symptoms of toxicity may not be reported by pediatric patients Close clinical monitoring of pediatric patients is recommended.
- Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Colistimethate should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Colistimethate is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may
(1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Colistimethate or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
ADVERSE REACTION
The following adverse reaction have been reported:
Gastrointestinal: gastrointestinal upset
Nervous System: tingling of extremities and tongue, slurred speech, dizziness, vertigo and paresthesia
Integumentary: generalized itching, urticaria and rash
Body as a whole: fever
Laboratory Deviations: increased blood urea nitrogen (BNU), elevated creatinine and decreased creatinine clearance
Respiratory System: respiratory distress and apnea
Renal System: nephrotoxicity and decreased urine output
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with colistimethate sodium can cause neuromuscular blockade characterized by paresthesia, lethargy, confusion, dizziness, ataxia, nystagmus, disorders of speech and apnea. Respiratory muscle paralysis may lead to apnea, respiratory arrest and death. Overdosage with the drug can also cause acute renal failure, manifested as decreased urine output and increase in serum concentrations of BNU and creatinine.
As in any case of overdose, colistimethate sodium therapy should be discontinued and general supportive measures should be utilized.
It is unknown whether colistimethate sodium can be removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis in overdose cases.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dose conversion
In the EU, the dose of colistimethate sodium (CMS) is prescribed and administered only as International Units (IU). The product label states the number of IU per vial.
Confusion and medication errors have occurred because of the different expressions of dose in terms of potency. The dose is expressed in the US, and other parts of the world, as milligrams of colistin base activity (mg CBA).
The following conversion table is prepared for information and the values must be considered nominal and approximate only.
Reconstitution for parenteral Administration: The vial content should be reconstituted with 2 mL sterile water for Injection accordingly. The reconstituted solution provides colistimethate sodium at a concentration equivalent to 34 mg/ml colistin base activity. During reconstitution swirl gently to avoid frothing. The Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. If these conditions are observed, the product should not be used.
Dosage
Adults and Pediatric Patients- Intravenous, Intramuscular or inhalation Administration: The dose of Colistimethate should be 2.5 to 5 mg/kg per day in 2 to 4 divided doses for patients with normal renal function, depending on the severity of the infection.
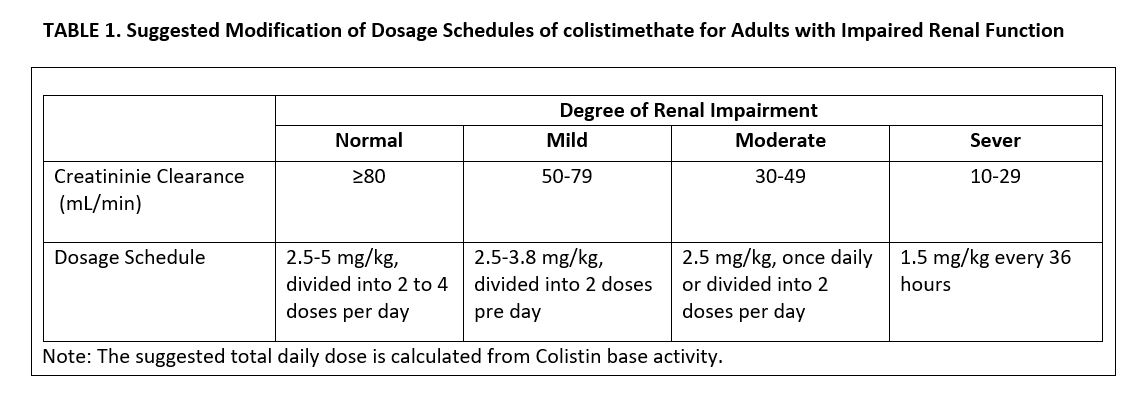
In obese individuals, dosage should be based on ideal body weight. The daily dose should be reduced in the presence of renal impairment. Modifications of dosage in the presence of renal impairment are presented in Table 1.
INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION
Direct Intermittent Administration- slowly inject one-half of the total daily dose over a period of 3 to 5 minutes every 12 hours.
Continuous Infusion- Slowly inject one-half of the total daily dose over 3 to 5 minutes. Add the remaining half of the total daily dose of Colistimethate to one of the following:
0.9% NaCl
5% dextrose in 0.9% NaCl
5% dextrose in water
5% dextrose in 0.45% NaCl
Lactated Ringer. solution
There are not sufficient data to recommend usage of Colistimethate with other drugs or other than the above listed infusion solutions.
Administer the second half of the total daily dose by slow intravenous infusion, starting 1 to 2 hours after the initial dose, over the next 22 to 23 hours. In the presence of impaired renal function, reduce the infusion rate depending on the degree of renal impairment.
The choice of intravenous solution and the volume to be employed are dictated by the requirements of fluid and electrolyte management.
INTRAMUSCULAR ADMINISTRATION
Reconstitute vial content with 2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, swirling gently to avoid frothing; final concentration provides colistimethate sodium equivalent to 34 mg/mL colistin base activity.
Inject IM deeply into a large muscle mass such as upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscles. Aspirate prior to injection to avoid injecting into a blood vessel.
Inhalation Administration
In Nebulized use of colistimethate sodium, the colistimethate sodium should be administered promptly after being mixed. Do not dissolve colistimethate sodium until ready to administer a dose.
NOTE: Vials for injection are used off-label for nebulization.
Nebulization of solution:
Using vials for injection: Reconstitute vial with 2 to 4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, swirling gently to avoid frothing. The dose should be inhaled over 10 to 15 minutes. Colistimethate sodium for inhalation should use with an appropriate nebulizer. For more detailed information on correct use of the selected nebuliser follow the instruction manual of the nebuliser. Inhalation should take place in a well ventilated room.
The solution is for single use only and any remaining solution should be discard.
HOW SUPPLIED
Colytex® (Colistimethate sodium) for injection, infusion or inhalation is supplied in box of 10 vials, each vial supplied as follows:
Colytex® 2,000,000 IU is a white to slightly yellow Iyophilized cake in a single dose glass vial with an aluminum cap and a dark blue flip-off cap.
STORAGE
Store below 30˚C. Protect from light.